Novel numerical optimization methodology paves the way for acoustic camouflaging in the form of sound source-shifters
Many of the techniques used in transformation optics have been applied to sound waves, giving rise to the parallel field of transformation acoustics.
In fact, researchers have already made substantial progress by developing the "acoustic cloak," the analog of the invisibility cloak for sounds.
While research on acoustic illusion has focused on the concept of masking the presence of an object, not much progress has been made on the problem of location camouflaging.
The concept of an acoustic source-shifter utilizes a structure that makes the location of the sound source appear different from its actual location.
Such devices capable of "acoustic location camouflaging" could find applications in advanced holography and virtual reality.
Unfortunately, the nature of location camouflaging has been scarcely studied, and the development of accessible materials and surfaces that would provide a decent performance has proven challenging.
Against this backdrop, Professor Garuda Fujii, affiliated with the Institute of Engineering and Energy Landscape Architectonics Brain Bank (ELab2) at Shinshu University, Japan, has now made progress in developing high-performance source-shifters.
In a recent study published in the Journal of Sound and Vibration online on May 5, 2023, Prof.
Fujii presented an innovative approach to designing source-shifter structures out of acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), an elastic polymer commonly used in 3D printing.
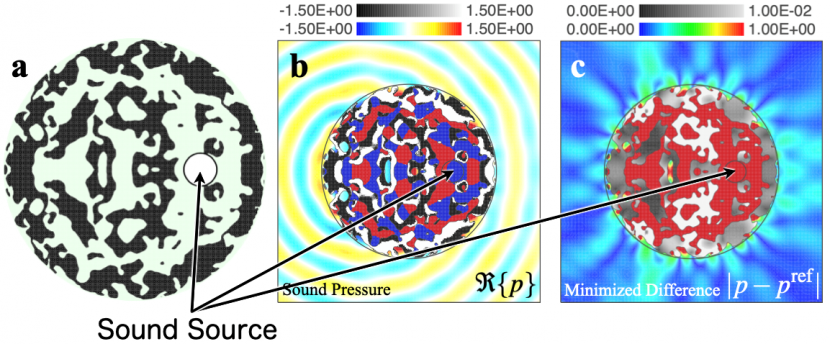
Prof. Fujii's approach is centered around a core concept: inverse design based on topology optimization.
The numerical approach builds on the reproduction of pressure fields (sound) emitted by a virtual source, i.e., the source that nearby listeners would mistakenly perceive as real.
Next, the pressure fields emitted by the actual source are manipulated to camouflage the location and make it sound as if coming from a different location in space.
This can be achieved with the optimum design of a metastructure that, by the virtue of its geometry and elastic properties, minimizes the difference between the pressure fields emitted from the actual and virtual sources.
Utilizing this approach, Prof. Fujii implemented an iterative algorithm to numerically determine the optimal design of ABS resin source-shifters according to various design criteria.
His models and simulations had to account for the acoustic-elastic interactions between fluids (air) and solid elastic structures, as well as the actual limitations of modern manufacturing technology.
The simulation results revealed that the optimized structures could reduce the difference between the emitted pressure fields of the masked source and those of a bare source at the virtual location to as low as 0.6%. "The optimal structure configurations obtained via topology optimization exhibited good performances at camouflaging the actual source location despite the simple composition of ABS that did not comprise complex acoustic metamaterials", remarks Prof.
Fujii.
To shed more light on the underlying camouflaging mechanisms, Prof.
Fujii analyzed the importance of the distance between the virtual and actual sources.
He found that a greater distance did not necessarily degrade the source-shifter's performance.
He also investigated the effect of changing the frequency of the emitted sound on the performance as the source-shifters had been optimized for only one target frequency.
Finally, he explored whether a source-shifter could be topologically optimized to operate at multiple sound frequencies.
While his approach requires further fine-tuning, the findings of this study will surely help advance illusion acoustics. He concludes, "The proposed optimization method for designing high-performance source-shifters will help in the development of acoustic location camouflage and the advancement of holography technology."